The term Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is a serious health condition that affects women. According to Center for Disease Control and Prevention, 1 in 8 women with a history of PID experiences serious difficulties getting pregnant. Have you heard of it before and you know its cause? Read more below:
What is PID?
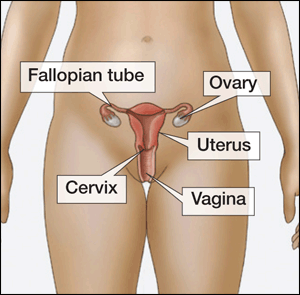
Pelvic inflammatory disease is an infection of a woman’s reproductive organs, such as the fallopian tube, uterus and the ovaries. PID is a common cause of pelvic pain in women. When it affects the uterus, it is called endometritis. For fallopian tubes, it is salpingitis, while for ovaries is oophoritis. It may also affect the pelvic peritoneum.
What causes PID?
PID is mostly caused by sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), such as Chlamydia infection or Gonorrhoea.
Other causes of PID include;
- Miscarriage
- Abortion
- IUCD users have a high incidence of PID. (IUCD (Intrauterine Contraceptive Device) is a device which is inserted into the uterus (womb) to prevent pregnancy.)
How can one contract PID?
You are more likely to contract PID if you;
• Have an STD and do not get treatment immediately;
• Have more than one sex partner;
• Have a sex partner who has sex other partners;
• Have had PID before;
• Are sexually active and around the age 25 or younger;
• Douche;
• Use an Intrauterine Contraceptive device (IUCD) for birth control.
Note: For IUCD users, according to Center for Disease Control (CDC), the small increased risk is mostly limited to the first three weeks after the IUCD is placed inside the uterus by a doctor.
Must read: Dangers Of Unprotected Sex
What are the symptoms of PID?
The symptoms include;
- Abdominal pain and tenderness
- Fever
- Irregular menstrual periods
- An unusual discharge with a bad odour from your vagina;
- Pain and/or bleeding when you have sex;
- Burning sensation when you urinate;
- Bleeding between periods.
How can one reduce the risk of getting PID?
If you are sexually active, you should do the following things to lower your chances of getting PID:
1. Being in a long-term mutually monogamous relationship with a partner who has been tested and has negative STD test results;
2. Using latex condoms the right way every time you have sex.
What are the treatments of PID?
PID can be treated if it is detected early. Your doctor will prescribe drugs to manage it symptomatically. That is antibiotics for infection and painkiller for pains.
It is advisable to treat your partner along too if your partner has STDs, and also avoid sexual intercourse throughout the course of the treatment.
You can contract PID again if you get infected with an STD again. Also, if you have had PID before, you have a higher chance of contracting it again.
If you don't treat yourself swiftly,
• It may cause scarring of the fallopian tube
• Ectopic pregnancy
• Infertility
Credit: Universal Nurse Tips

Comments